Retirement planning is a crucial aspect of financial management that requires thoughtful consideration and strategic actions. As we advance through 2024, the landscape of retirement planning continues to evolve, influenced by economic trends, policy changes, and technological advancements. Whether you’re just starting your career or nearing retirement age, understanding the latest strategies and best practices can help ensure a secure and comfortable retirement. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore key tips for retirement planning in 2024 to help you navigate this important financial milestone effectively.
1. Start Early: The Power of Compound Interest
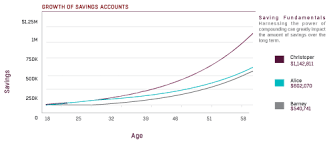
1.1 Why Starting Early Matters
One of the most fundamental principles of retirement planning is the power of compound interest. The earlier you start saving for retirement, the more time your investments have to grow. Compound interest allows your money to generate earnings on both the initial principal and the accumulated interest, leading to exponential growth over time.
1.2 Setting Up a Retirement Savings Plan
- 401(k) Plans: If your employer offers a 401(k) plan, take advantage of it. Contributing to a 401(k) provides tax advantages and often comes with employer matching, which is essentially free money for your retirement.
- IRA Accounts: Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) offer another avenue for retirement savings. Traditional IRAs provide tax-deductible contributions, while Roth IRAs offer tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
1.3 Tips for Maximizing Early Savings
- Automate Contributions: Set up automatic contributions to your retirement accounts to ensure consistent saving without the need for manual intervention.
- Increase Contributions Gradually: As your income grows, gradually increase your contributions to keep up with inflation and maximize your retirement savings.
2. Diversify Your Investment Portfolio
2.1 Importance of Diversification
Diversifying your investment portfolio is essential to managing risk and maximizing returns. A well-diversified portfolio includes a mix of asset classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and cash.
2.2 Key Investment Options
- Stocks: Investing in stocks provides growth potential but comes with higher risk. Consider investing in a diversified mix of individual stocks or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) to spread risk.
- Bonds: Bonds offer more stable returns compared to stocks and can provide income through interest payments. Consider including a mix of government and corporate bonds in your portfolio.
- Real Estate: Real estate investments, such as rental properties or real estate investment trusts (REITs), can provide rental income and potential appreciation.
- Cash and Cash Equivalents: Maintaining a portion of your portfolio in cash or cash equivalents (e.g., money market funds) provides liquidity and stability.
2.3 Rebalancing Your Portfolio
Regularly review and rebalance your investment portfolio to ensure it aligns with your retirement goals and risk tolerance. Rebalancing involves adjusting the allocation of assets to maintain your desired risk level and investment strategy.
3. Consider Your Retirement Age and Lifestyle
3.1 Determining Your Retirement Age
Deciding when to retire is a critical aspect of retirement planning. Factors such as your financial situation, health, and personal goals will influence this decision. Consider the following:
- Social Security Benefits: Your Social Security benefits are influenced by the age at which you start claiming them. The longer you wait, the higher your monthly benefits will be.
- Pension Plans: If you have a pension plan, review its terms to understand how early retirement might impact your benefits.
3.2 Planning for Retirement Lifestyle
Think about the lifestyle you want to maintain in retirement. This includes considering:
- Living Expenses: Estimate your monthly expenses in retirement, including housing, healthcare, travel, and leisure activities.
- Healthcare Costs: Anticipate potential healthcare expenses, including insurance premiums, out-of-pocket costs, and long-term care.
- Debt Management: Aim to reduce or eliminate debt before retirement to ease financial stress and increase your disposable income.
4. Stay Informed About Tax Implications
4.1 Understanding Tax-Advantaged Accounts
Different retirement accounts come with various tax advantages. Familiarize yourself with the tax implications of each type:
- 401(k) and Traditional IRA: Contributions are typically tax-deductible, but withdrawals during retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
- Roth IRA: Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, but qualified withdrawals are tax-free.
4.2 Tax-Efficient Withdrawal Strategies
Develop a strategy for withdrawing funds from your retirement accounts in a tax-efficient manner. This may involve:
- Minimizing Taxable Withdrawals: Withdraw funds from accounts in a way that minimizes your overall tax burden. For example, consider drawing from Roth accounts first to avoid increasing your taxable income.
- Understanding Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): Be aware of the RMD rules for retirement accounts. Starting at age 73, you must begin taking distributions from your traditional IRA or 401(k).
5. Leverage Technology and Tools
5.1 Retirement Planning Tools
Utilize technology and online tools to enhance your retirement planning:
- Retirement Calculators: Use online calculators to estimate how much you need to save and how your savings will grow over time.
- Budgeting Apps: Track your expenses and income using budgeting apps to ensure you stay on track with your savings goals.
- Investment Platforms: Consider using robo-advisors or investment platforms that offer automated portfolio management and financial planning.
5.2 Stay Updated with Financial News
Regularly follow financial news and updates to stay informed about changes in retirement planning strategies, tax laws, and investment opportunities.
6. Consult with a Financial Advisor
6.1 The Role of a Financial Advisor
A financial advisor can provide personalized guidance and help you develop a comprehensive retirement plan. They can assist with:
- Investment Planning: Creating and managing a diversified investment portfolio based on your risk tolerance and goals.
- Tax Planning: Offering strategies to optimize tax efficiency and minimize tax liabilities.
- Estate Planning: Assisting with estate planning to ensure your assets are distributed according to your wishes.
6.2 Choosing the Right Advisor
When selecting a financial advisor, consider their qualifications, experience, and fee structure. Look for advisors who are certified financial planners (CFPs) and have a fiduciary responsibility to act in your best interest.
7. Plan for Unexpected Events
7.1 Building an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is essential for handling unexpected expenses and financial setbacks. Aim to save three to six months’ worth of living expenses in a readily accessible account.
7.2 Insurance Considerations
Ensure you have adequate insurance coverage to protect yourself and your assets:
- Health Insurance: Review your health insurance options, including Medicare and supplemental policies.
- Long-Term Care Insurance: Consider long-term care insurance to cover potential costs associated with assisted living or nursing home care.
- Life Insurance: Evaluate your life insurance needs to provide financial security for your loved ones.
Conclusion
Retirement planning is a dynamic process that requires careful consideration and ongoing adjustments. By starting early, diversifying your investments, and staying informed about tax implications and technological advancements, you can build a solid foundation for a comfortable and secure retirement. Additionally, leveraging the expertise of financial advisors and planning for unexpected events will further enhance your readiness for retirement. As you navigate your retirement journey in 2024, these key tips will help you make informed decisions and achieve your financial goals with confidence.


